A critical and consistent feature of repeat victimization is that repeat offenses occur quickly-many repeats occur within a week of the initial offense, and some even occur within 24 hours. An early study of RV showed the highest risk of a repeat burglary was during the first week after an initial burglary.24
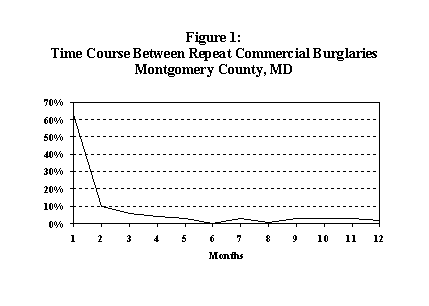
After the initial period of heightened risk, the risk of a repeat offense declines rapidly until the victim once again has about the same victimization risk as persons or properties that have never been victimized. This common pattern is displayed in Figure 1 and shows that 60 percent of repeat burglaries occurred within one month of the initial offense; about 10 percent occurred during the second month. After the second month, the likelihood of a repeat offense is quite low.
RV consistently demonstrates a predictable pattern known as time course: a relatively short high-risk period is followed by a rapid decline and then a leveling off of risk. The length of the time period of heightened victimization risk varies based on local crime problems. Determining the time period of heightened risk is critical because any preventive actions must be taken during the high risk period to prevent subsequent offenses. For offenses with a short high-risk time course, the preventive actions must be taken very quickly. The delay of two days or a week may miss the opportunity to prevent a repeat from occurring.
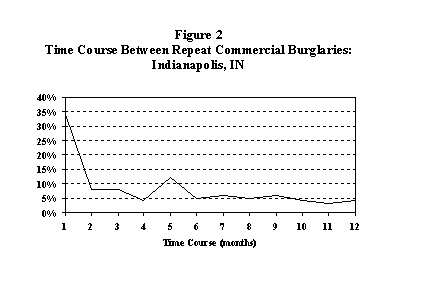
Some research suggests that the predictable time course of repeat victimization may be punctuated by a "bounce"-a slight resurgence in the proportion of revictimization occurring after the risk appears to be steadily declining (see Figure 2). The bounce in the time course may be associated with the replacement of property with insurance money. It seems likely that some repeat offenders may employ a "cool down" period, perceiving victims to be on high alert immediately after an offense but relaxing their vigilance within a few months.
Evidence suggests that the time period between an initial and subsequent offense varies by the type of crime. The time course of domestic violence appears short (see Table 7) with 15% of repeat offenses occurring within a day. The time course of RV may be calculated by hours, days, weeks or months, or even years between offenses, depending upon the temporal distribution of data.
In addition to variation by crime type, it is likely that the time course may also vary by the location of the study. For example, a study in Florida showed 25% of repeat burglaries took place within a week while a study in Merseyside showed 11% of repeats occurred during a similar time period.
Although the time period for reporting repeat victimization varies, the statement of such findings is straightforward. For example, the first row in Table 7 would be stated as:
Of repeat incidents of domestic violence, 15% occurred within 24 hours of the initial incident while 35% of repeat incidents occurred within five weeks.
Table 7: Time Course of Repeat Victimization by Offense Type:
Crime Reports
Offense |
Proportion of Repeats by Time Period |
Where/Study |
|---|---|---|
Domestic violence |
15% within 24 hours 35% within five weeks |
Merseyside, England25 |
Bank robbery |
33% within three months |
England26 |
Residential burglary |
25% within a week 51% within a month |
Tallahassee, Florida27 |
11% within one week 33% within one month |
Merseyside, England28 |
|
Non-residential burglary |
17% within one week 43% within one month |
Merseyside, England29 |
Property crime at schools |
70% within a month |
Merseyside, England30 |
There are two primary reasons for repeat victimization: one, known as the "boost" explanation, relates to the role of repeat offenders; the other, known as the "flag" explanation, relates to the vulnerability or attractiveness of certain victims.
In the flag explanation, some targets are unusually attractive to criminals or particularly vulnerable to crime, and these characteristics tend to remain constant over time. In such cases, the victim is repeatedly victimized by different offenders.
In the boost explanation, repeat victimization reflects the successful outcome of an initial offense. Specific offenders gain important knowledge about a target from their experience and use this information to reoffend.
This knowledge may include easy access to a property, times during which a target is unguarded, or techniques for overcoming security. For example, offenders who steal particular makes of vehicles may have knowledge of ways to defeat their electronic security systems or locking mechanisms. Even fraudulent victimization shows this boost pattern, as insurance fraud may explain some cases of repeat victimization.
Boost and flag explanations may overlap and vary by offense type. For example, bank robberies are most likely to recur if an initial robbery yielded a large take; when monetary losses were small, banks were less likely to be robbed again.34 Research on repeat victimization-for banks and other targets-suggests that most offenses are highly concentrated on a small number of victims while the majority of targets are never victimized at all.
Research has revealed several types of repeat victimization:
For some crimes, repeat victimization is related to other common crime patterns:
These crime patterns are not mutually exclusive and may intersect or overlap; the detection of repeat victimization, however, routinely provides important clues about the reasons for recurrence and permits police to focus on avenues for prevention.
For many crime problems, repeat victimization is most common in high crime areas.
† Offenses such as domestic violence and sexual assault do not usually exhibit spatial concentrations, while other targets of repeat victimization, such as convenience stores, budget motels, and banks, may be geographically dispersed.
Persons and places in high crime areas face a greater risk of initial victimization for many crimes, and they may lack the means to block a subsequent offense by improving security measures and doing so quickly.35
In high crime areas, crime is so concentrated among repeat victims that recurring offenses can create hot spots-relatively small geographic areas in which offenses are clustered. As a result, experts have coined the term "hot dots" because incident maps may be dominated by symbols scaled to represent the number of offenses at specific addresses.36 (See Figure 3.)
Figure 3
Repeat Commercial Robberies37
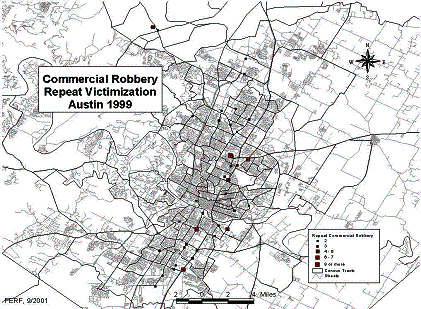
Incident maps are often used to identify hot spots and can be used to detect repeat victimization. Icons or symbols should be used on maps that are scaled in size to reflect the number of incidents, otherwise points that overlap may not be visible, masking RV. Data decisions can also distort the amount of repeat victimization that can be detected on maps. Short time periods, such as a week or month or even a quarter-may mask repeat victimization; imprecise address information, such as a single address for incidents occurring at a large apartment complex, also mask specific locations of RV.
Incident maps may mask RV in densely populated areas because most maps demonstrate the incidence and spatial distribution of offenses, and do not account for the concentration of crimes. In densely populated areas such as those with multi-family dwellings, most maps will not differentiate between apartment units and apartment buildings that may comprise large apartment complexes.
Crime is not always geographically patterned, and this is also true for repeat victimization. For example, victims of domestic violence are unlikely to be geographically concentrated. Even repeat incidents of domestic violence may not occur at a single address; one offense may take place at a residence while the repeat offense may occur at a victim's workplace.
Some crimes, such as burglary, are clustered geographically; repeat burglaries are even more predictably clustered.38 Thus, citywide data on burglaries may mask the proportion of repeat burglaries occurring in smaller geographic areas. This suggests the need to use different geographic levels of analysis to examine RV. In contrast to burglary, offenses such as bank robberies and domestic violence may necessitate the use of data from the entire jurisdiction.
Although the phenomenon of repeat victimization is well-established, it is easy to overlook the importance of repeat victimization in crime pattern analysis because most people and properties within a jurisdiction are not victimized by crime, particularly within a period of one or a few years.
Consider a study in which 10,828 burglaries were reported to police in 1990:39
At first, repeat victimization appears minimal:
Analysis sheds further light on revictimization:
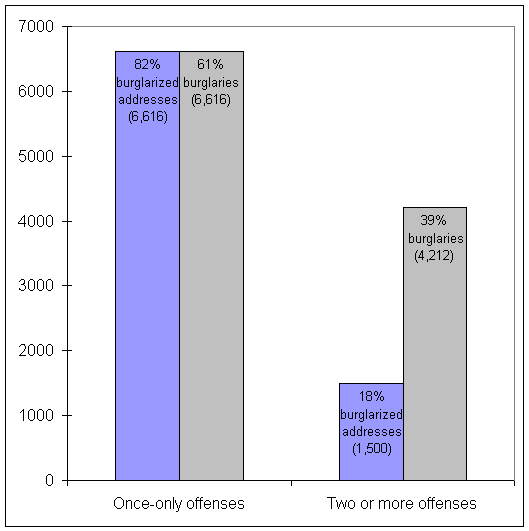
While repeat victimization may still appear minimal, Figure 4 demonstrates graphically that revictimization accounts for a disproportionately large share of all burglaries: 18 percent of victims accounted for 39 percent of burglaries. If offenses after the initial offense had been prevented, the jurisdiction would have experienced 2,712 fewer burglaries-a 25 percent reduction in burglaries.
Figure 4:
Distribution of Burglaries by Address and Frequency
In addition to its potential for crime reduction, analysis of repeat victimization provides an important analytic and management tool for police organizations by serving the following purposes:
Although recognizing repeat victimization is an important step, working out precisely what to do about revictimization will require additional effort on the part of police.
Once an agency undertakes analysis of repeat victimization and determines the prevalence and time course of repeats by offense type, the crime pattern can be used as a tool for developing responses to reduce revictimization. Focusing on victims raises a number of special concerns that police should consider:
You may order free bound copies in any of three ways:
Online: Department of Justice COPS Response Center
Email: askCopsRC@usdoj.gov
Phone: 800-421-6770 or 202-307-1480
Allow several days for delivery.
Send an e-mail with a link to this guide.
* required
Error sending email. Please review your enteries below.